Java SE 第七章泛型和合集--集合类--List接口、Set接口、Map接口
本文共 5143 字,大约阅读时间需要 17 分钟。
一、List接口
说明: 1)该接口继承Collection接口 2)元素允许重复 3)以元素添加的次序来放置元素,不会重新排列 4)支持位置索引随机操作 List接口的具体实现类常用的有ArrayList和LinkList。 1、ArrayList支持可随需要而调整的动态数组。 其内部封装了一个动态可再分配的Object[]数组。 每个ArrayList对象都有一个capacity,表示存储列表中元素的数组的容量。 常用方法: ArrayList() Array List(Collection<?extends E>c) ArrayList(int capacity) void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) void trimToSize() 示例:基于String类型演示泛型ArrayList的常用操作,包括增加、删除、修改、遍历。package ch07;import java.util.*;public class ArrayListDemo { public static ArrayList arrayList; //初始化链表 public static void init(){ arrayList=new ArrayList (4); System.out.println("初始化长度:"+arrayList.size()); arrayList.add("First"); arrayList.add("second"); arrayList.add("third"); arrayList.add("Forth"); } //打印链表信息 public static void printInfo(){ System.out.println("增加元素后的长度:"+arrayList.size()); ArrayList arrayList2=new ArrayList (arrayList); System.out.println("arrayList:"+arrayList); System.out.println("arrayList2"+arrayList2); } //对链表实现修改、删除操作 public static void modify(){ arrayList.add(1,"insert data"); System.out.println("增加元素后的长度:"+arrayList.size()); arrayList.remove("second"); System.out.println("删除‘second’后的长度:"+arrayList.size()); arrayList.remove(2); System.out.println("删除第3个元素后的长度:"+arrayList.size()); arrayList.remove("nothing"); System.out.println("删除‘nothing’后的长度:"+arrayList.size()); } public static void toArray(){ Object[]arr=arrayList.toArray(); for(int i=0;i 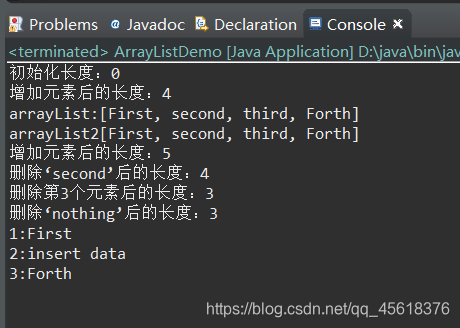
public static void travel(){ System.out.println("遍历前的长度:"+arrayList.size()); Iterator iterator=arrayList.iterator(); int i=0; while(iterator.hasNext()){ String str=iterator.next(); i++; System.out.println(str); if(i%3==0){ iterator.remove(); } } System.out.println("删除后的长度:"+arrayList.size()); 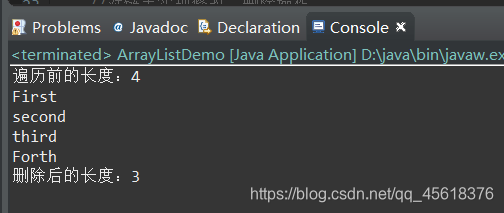
for(string str:arrayList){ System.out.println(str);} 二、Set接口
说明: 1)该接口继承Collection接口 2)允许重复 3)没有引入新方法,所以Set就是一个Collection,只是其行为不同 具体实现类:HashSet、TreeSet 1、HashSet(散列) 能快速定位一个元素,一般需要重写hashCode()方法。 构造方法列表: HashSet() HashSet(Collection<?extends E>c) HashSet(int capacity) HashSet(int capacity,float fill) 示例:基于String类型演示泛型HashSet的使用public static void main(String[] args) { HashSet hashSet=new HashSet (); hashSet.add("first"); hashSet.add("second"); hashSet.add("third"); hashSet.add("forth"); System.out.println(hashSet); for(String str:hashSet){ System.out.println(str); } 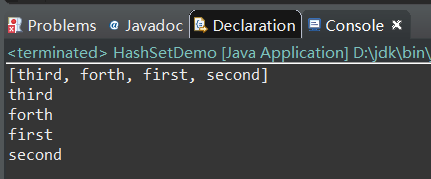
public static void main(String[] args) { TreeSet treeSet=new TreeSet (); treeSet.add("first"); treeSet.add("second"); treeSet.add("third"); treeSet.add("forth"); System.out.println(treeSet); for(String str:treeSet) { System.out.println(str); } } 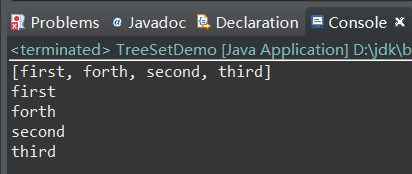
public static void main(String[] args) { HashMap hashMap=new HashMap (); hashMap.put("Tom", new Integer(23)); hashMap.put("Rose", new Integer(18)); hashMap.put("Jane", new Integer(26)); hashMap.put("Black", new Integer(24)); hashMap.put("Smith", new Integer(21)); Set >set=hashMap.entrySet(); for(Map.Entry entry:set){ System.out.println(entry.getKey()+":"+entry.getValue()); } System.out.println("---------------"); Set KeySet=hashMap.keySet(); StringBuffer buffer=new StringBuffer(""); for(String str:KeySet){ buffer.append(str+','); } String str=buffer.substring(0,buffer.length()-1); System.out.println(str); } 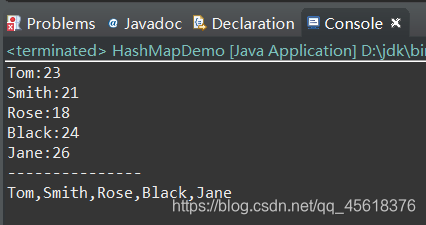
public static void main(String[] args) { TreeMap treeMap=new TreeMap (); treeMap.put("Tom", new Integer(23)); treeMap.put("Rose", new Integer(18)); treeMap.put("Jane", new Integer(26)); treeMap.put("Black", new Integer(24)); treeMap.put("Smith", new Integer(21)); Set >set=treeMap.entrySet(); for(Entry entry:set){ System.out.println(entry.getKey()+":"+entry.getValue()); } System.out.println("-----------"); Set KeySet=treeMap.keySet(); StringBuffer buffer=new StringBuffer(""); for(String str:KeySet) { buffer.append(str+","); } String str=buffer.substring(0,buffer.length()-1); System.out.println(str); } 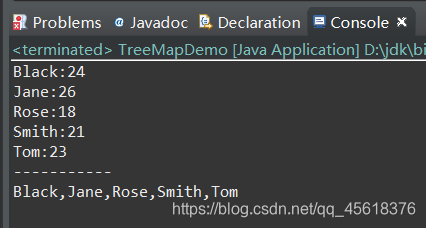
转载地址:http://edyg.baihongyu.com/
你可能感兴趣的文章
MySQL 高可用性之keepalived+mysql双主
查看>>
mysql-connector-java各种版本下载地址
查看>>
mysql-group_concat
查看>>
MySQL-【4】基本操作
查看>>
Mysql-丢失更新
查看>>
Mysql-事务阻塞
查看>>
Mysql-存储引擎
查看>>
mysql-开启慢查询&所有操作记录日志
查看>>
MySQL-数据目录
查看>>
MySQL-数据页的结构
查看>>
MySQL-架构篇
查看>>
MySQL-索引的分类(聚簇索引、二级索引、联合索引)
查看>>
Mysql-触发器及创建触发器失败原因
查看>>
MySQL-连接
查看>>
mysql-递归查询(二)
查看>>
MySQL5.1安装
查看>>
mysql5.5和5.6版本间的坑
查看>>
mysql5.5最简安装教程
查看>>
mysql5.6 TIME,DATETIME,TIMESTAMP
查看>>
mysql5.6.21重置数据库的root密码
查看>>